На Aliexpress представлено большое количество разнообразных внешних модулей RTC и комбинированных модулей RTC + SD карта или EEPROM. Рассмотрю наиболее интересные для использования с компактными девелоперскими платами MH ET Live Minikit (ESP32) (другой вариант поиска) или Wemos D1 mini (ESP8266).
Tiny RTC с EEPROM на 32 кБит

- Tiny RTC с EEPROM на 32 кБит:
- RTC на чипе DS1307. Напряжение питания чипа 5 V.
- Память EEPROM 32 кБит (чип AT24C32).
- Выводы не совпадают с платой Wemos D1 mini, хотя по габаритам и совместима, поэтому использовать её неудобно.
- Модуль RTC использует интерфейс I2C, однако выставить на плате адрес шины нельзя.
- Размеры модуля, мм: 28×25.
- Батарея для питания: CR2032
- Цена с доставкой в Россию: 0,34 USD
- Модуль доступен у большого количества поставщиков на Aliexpress.
Основной плюс платы — низкая цена и наличие распаянного на плате EEPROM чипа. В некоторых случаях значительная емкость SD карты не нужна и переплачивать из-за этого лишние 300 руб не хочется.
К сожалению нормального варианта этого модуля, который бы «садился» на разъем девеоперских плат найти не удалось.
RTC + SD card reader module
 | 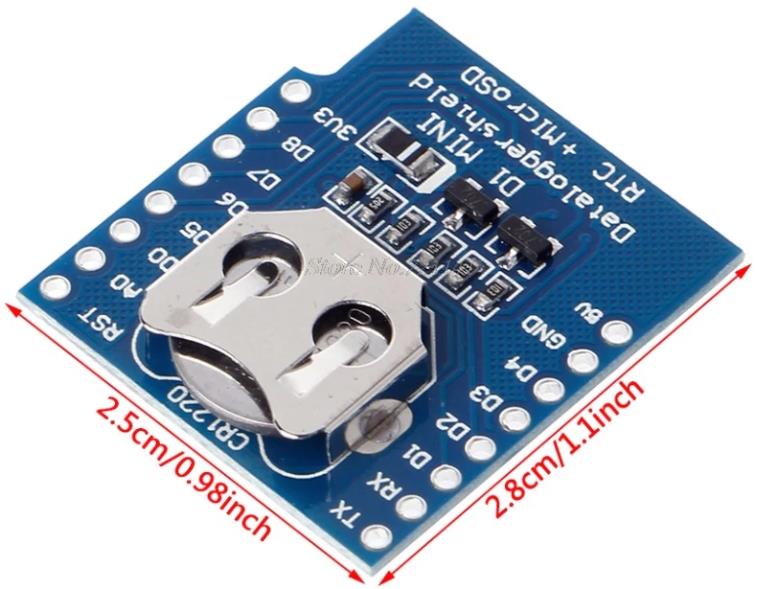 |
- RTC + SD card reader module для платы Wemos D1 mini (ESP8266) или MH ET Live Minikit (ESP32):
- RTC на чипе DS1307. Напряжение питания чипа 5 V.
- Слот Micro SD карты для логирования.
- Модуль RTC использует интерфейс I2C, однако выставить на плате адрес шины нельзя.
- Размеры модуля, мм: 28×25.
- Батарея для питания: CR1220
- Цена с доставкой в Россию: 1,55 USD
- Судя по всему разработка компании RobotDyn. Там-же есть вариант модуля без SD карты.
- В разделе документации доступны схемы.
- Модуль доступен у большого количества поставщиков на Aliexpress.
Функционально второй модуль удобнее из-за наличия слота SD карты и возможности каскадирования («сэндвич») при использовании компактных девелоперских плат MH ET Live Minikit (ESP32) или Wemos D1 mini (ESP8266). Рассмотрю работу с этим модулем подробнее.
Схема для подключения не требуется, поскольку при стекировании девелоперских плат с Wemo D1 mini datalogger нужные пины уже состыкованы. Для подключения RTC пины:
| Wemos D1 mini (ESP8266) | Описание | ESP32 |
| D1 (GPIO5) | SCL | GPIO 22 (SCL) |
| D2 (GPIO4) | SDA | GPIO 21 (SDA) |
| 5V | 5V | |
| 3.3V | 3.3V | |
| GND | GND |
Ещё раз обращаю внимание, что питание чипа RTC — 5 V. Если его запитать от 3,3 V, то он работает некорректно. Не выдает ошибки при соединении, но при запросе даты — выдает некорректную.
SD карта запитывается от пина 3.3V. При подключении к ESP32 не нужно забывать подключать это напряжение.
Data logger RTC shield (Wemos D1 mini) НЕЛЬЗЯ использоваить при питании от аккумулятора 3.7 V. 🙁
Для подключения SD карты к ESP8266/ESP32:
| Wemos D1 mini (ESP8266) | Описание | ESP32 VSPI | ESP32 HSPI |
| D5 (GPIO 14) | CLK/SCK | GPIO18 | GPIO14 |
| D6 (GPIO 12) | DO/MISO | GPIO19 | GPIO12 |
| D7 (GPIO13) | DI/MOSI | GPIO23 | GPIO13 |
| D8 (GPIO 15) | CS/SS | GPIO5 | GPIO15 |
Выводы SD карты подключаются к выводам Wemos D1 без каких-либо дополнительных схем защиты от статического электричества. Например, диодной сборкой SMF05C.
Программа
Для работы с модулем Wemos D1 mini RTC + SD card datalogger использовал следующий код из библиотеки https://github.com/Makuna/Rtc.
Библиотека Adafruit не работает.
// CONNECTIONS:
// DS1307 SDA --> SDA
// DS1307 SCL --> SCL
// DS1307 VCC --> 5v
// DS1307 GND --> GND
/* for software wire use below
#include <SoftwareWire.h> // must be included here so that Arduino library object file references work
#include <RtcDS1307.h>
SoftwareWire myWire(SDA, SCL);
RtcDS1307<SoftwareWire> Rtc(myWire);
for software wire use above */
/* for normal hardware wire use below */
#include <Wire.h> // must be included here so that Arduino library object file references work
#include <RtcDS1307.h>
RtcDS1307<TwoWire> Rtc(Wire);
/* for normal hardware wire use above */
void setup ()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.print("compiled: ");
Serial.print(__DATE__);
Serial.println(__TIME__);
//--------RTC SETUP ------------
// if you are using ESP-01 then uncomment the line below to reset the pins to
// the available pins for SDA, SCL
// Wire.begin(0, 2); // due to limited pins, use pin 0 and 2 for SDA, SCL
Rtc.Begin();
RtcDateTime compiled = RtcDateTime(__DATE__, __TIME__);
printDateTime(compiled);
Serial.println();
if (!Rtc.IsDateTimeValid())
{
if (Rtc.LastError() != 0)
{
// we have a communications error
// see https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WireEndTransmission for
// what the number means
Serial.print("RTC communications error = ");
Serial.println(Rtc.LastError());
}
else
{
// Common Cuases:
// 1) first time you ran and the device wasn't running yet
// 2) the battery on the device is low or even missing
Serial.println("RTC lost confidence in the DateTime!");
// following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
// it will also reset the valid flag internally unless the Rtc device is
// having an issue
Rtc.SetDateTime(compiled);
}
}
if (!Rtc.GetIsRunning())
{
Serial.println("RTC was not actively running, starting now");
Rtc.SetIsRunning(true);
}
RtcDateTime now = Rtc.GetDateTime();
if (now < compiled)
{
Serial.println("RTC is older than compile time! (Updating DateTime)");
Rtc.SetDateTime(compiled);
}
else if (now > compiled)
{
Serial.println("RTC is newer than compile time. (this is expected)");
}
else if (now == compiled)
{
Serial.println("RTC is the same as compile time! (not expected but all is fine)");
}
// never assume the Rtc was last configured by you, so
// just clear them to your needed state
Rtc.SetSquareWavePin(DS1307SquareWaveOut_Low);
}
void loop ()
{
if (!Rtc.IsDateTimeValid())
{
if (Rtc.LastError() != 0)
{
// we have a communications error
// see https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WireEndTransmission for
// what the number means
Serial.print("RTC communications error = ");
Serial.println(Rtc.LastError());
}
else
{
// Common Cuases:
// 1) the battery on the device is low or even missing and the power line was disconnected
Serial.println("RTC lost confidence in the DateTime!");
}
}
RtcDateTime now = Rtc.GetDateTime();
printDateTime(now);
Serial.println();
delay(10000); // ten seconds
}
#define countof(a) (sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]))
void printDateTime(const RtcDateTime& dt)
{
char datestring[20];
snprintf_P(datestring,
countof(datestring),
PSTR("%02u/%02u/%04u %02u:%02u:%02u"),
dt.Month(),
dt.Day(),
dt.Year(),
dt.Hour(),
dt.Minute(),
dt.Second() );
Serial.print(datestring);
}Код не требует какой-либо настройки и начинает работать сразу.
Работа с Wemos D1 mini Datalogger через I2C (библиотека Wire.h) без использования дополнительных библиотек.
#include "Wire.h"
#define DS1307_I2C_ADDRESS 0x68
byte decToBcd(byte val)
{
return ( (val/10*16) + (val%10) );
}
byte bcdToDec(byte val)
{
return ( (val/16*10) + (val%16) );
}
void setDateDs1307(byte second, // 0-59
byte minute, // 0-59
byte hour, // 1-23
byte dayOfWeek, // 1-7
byte dayOfMonth, // 1-28/29/30/31
byte month, // 1-12
byte year) // 0-99
{
Wire.beginTransmission(DS1307_I2C_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0);
Wire.write(decToBcd(second));
Wire.write(decToBcd(minute));
Wire.write(decToBcd(hour));
Wire.write(decToBcd(dayOfWeek));
Wire.write(decToBcd(dayOfMonth));
Wire.write(decToBcd(month));
Wire.write(decToBcd(year));
Wire.endTransmission();
}
void getDateDs1307(byte *second,
byte *minute,
byte *hour,
byte *dayOfWeek,
byte *dayOfMonth,
byte *month,
byte *year)
{
Wire.beginTransmission(DS1307_I2C_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0);
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(DS1307_I2C_ADDRESS, 7);
*second = bcdToDec(Wire.read() & 0x7f);
*minute = bcdToDec(Wire.read());
*hour = bcdToDec(Wire.read() & 0x3f);
*dayOfWeek = bcdToDec(Wire.read());
*dayOfMonth = bcdToDec(Wire.read());
*month = bcdToDec(Wire.read());
*year = bcdToDec(Wire.read());
}
void setup()
{
byte second, minute, hour, dayOfWeek, dayOfMonth, month, year;
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
second = 45;
minute = 3;
hour = 7;
dayOfWeek = 5;
dayOfMonth = 17;
month = 4;
year = 8;
setDateDs1307(second, minute, hour, dayOfWeek, dayOfMonth, month, year);
}
void loop()
{
byte second, minute, hour, dayOfWeek, dayOfMonth, month, year;
getDateDs1307(&second, &minute, &hour, &dayOfWeek, &dayOfMonth, &month, &year);
Serial.print(hour, DEC);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(minute, DEC);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(second, DEC);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(month, DEC);
Serial.print("/");
Serial.print(dayOfMonth, DEC);
Serial.print("/");
Serial.print(year, DEC);
Serial.print(" Day_of_week:");
Serial.println(dayOfWeek, DEC);
delay(1000);
}Micro SD карта на Wemos D1 mini datalogger
Схема для подключения модуля по-прежнему не нужна. 🙂 Все соединения работают нормельно после сборки «сэндвича» из
Wemos D1 mini (ESP8266) и Wemos D1 mini datalogger.
Проверил работу штатной библиотеки ESP8266 для работы с Micro SD картой. Тестовый пример без проблем откомпилировался и отработал. Так что модуль работает без проблем.
ВАЖНЫЙ МОМЕНТ РАБОТЫ SD карты с ESP8266!!!
Я использовал Samsung 32Gb EVO Plus отформатированную в FAT32 и с ней DataLogger не инициализировал карту. После того как отформатировал в FAT16 ESP8266 стал читать SD карту.
При этом на дешевой Micro SD «SP Elite» 16 Gb отформатированной в FAT32 проблем с чтением не возникло, ESP8266 без проблем проинициализировал карту.
В коде ниже нужно обратить внимание на CS PIN инициализации SD.init(15). На Wemos Mini D1 пин CS заведен на GPIO15, а не GPIO4.
/*
SD card read/write
This example shows how to read and write data to and from an SD card file
The circuit:
SD card attached to SPI bus as follows:
** MOSI - pin 11
** MISO - pin 12
** CLK - pin 13
** CS - pin 4
created Nov 2010
by David A. Mellis
modified 9 Apr 2012
by Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
*/
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
File myFile;
void setup() {
// Open serial communications and wait for port to open:
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for Leonardo only
}
Serial.print("Initializing SD card...");
if (!SD.begin(4)) {
Serial.println("initialization failed!");
return;
}
Serial.println("initialization done.");
// open the file. note that only one file can be open at a time,
// so you have to close this one before opening another.
myFile = SD.open("test.txt", FILE_WRITE);
// if the file opened okay, write to it:
if (myFile) {
Serial.print("Writing to test.txt...");
myFile.println("testing 1, 2, 3.");
// close the file:
myFile.close();
Serial.println("done.");
} else {
// if the file didn't open, print an error:
Serial.println("error opening test.txt");
}
// re-open the file for reading:
myFile = SD.open("test.txt");
if (myFile) {
Serial.println("test.txt:");
// read from the file until there's nothing else in it:
while (myFile.available()) {
Serial.write(myFile.read());
}
// close the file:
myFile.close();
} else {
// if the file didn't open, print an error:
Serial.println("error opening test.txt");
}
}
void loop() {
// nothing happens after setup
}Подключение SD карты к ESP32 описано здесь. В цело все то-же самое. Проблем возникнуть не должно.
Полезные ссылки
- Wemos D1 mini datalogger (DS1307 + SD card) schematic and description.
- Размеры модуля Wemos D1 mini datalogger (DS1307 + SD card).
- Библиотека для работы с DS1307.
- Видеообзор модуля Wemos D1 mini datalogger (DS1307 + SD card) на русском.
- Подключение SD карты к ESP32 от разработчиков Espressif.
- Подключение SD карты к ESP32.
- ESP32 Pinout Reference: Which GPIO pins should you use?